Congenital Syphilis
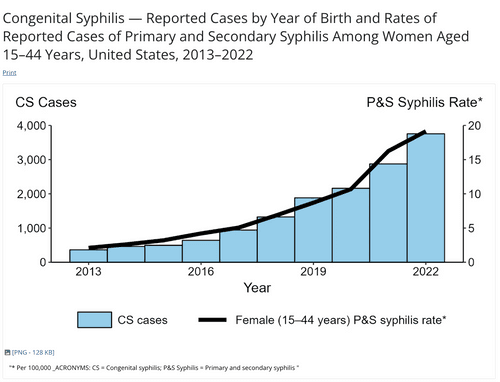
This chart is a publication of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). January, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/std/statistics/2022/figures/cs-1.htm
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacteria Treponema pallidium (T. Pallidium). Untreated or inadequately treated syphilis during pregnancy can result in congenital syphilis.
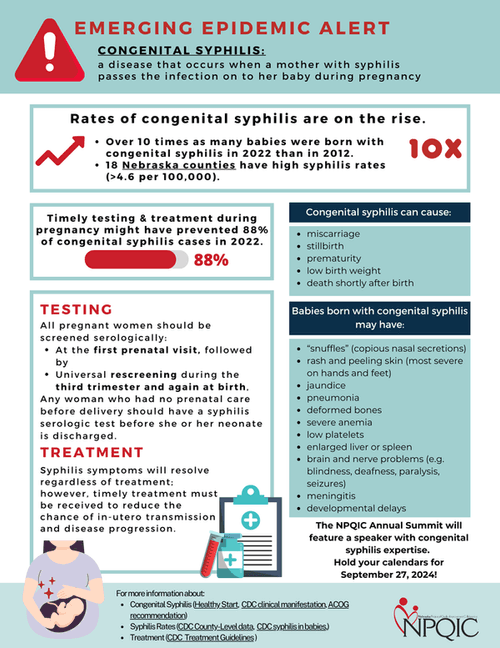
Congenital syphilis is a significant cause of neonatal morbidity and mortality worldwide and can result in miscarriage, stillbirth, prematurity, low birth weight, severe lifelong health problems, and neonatal death.
Rates of syphilis are on the rise in the United States and within Nebraska, resulting in over ten times as many babies born with congenital syphilis in 2022 than in 2012 (MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep, 2023). Many Nebraska counties have high rates (>4.6 per 100,000) of syphilis.
Currently, the CDC recommends screening all pregnant people at least once during their pregnancy and taking an individual, risk-based approach to syphilis screening for others. For many people, the most significant risk factor for syphilis is living in a county with high rates of syphilis.
Update: In April 2024, ACOG issued a new practice advisory recommending that all pregnant people be screened serologically for syphilis at the first prenatal care visit, followed by universal rescreening during the third trimester and again at birth.
Screening all pregnant women for syphilis and providing early treatment for women with syphilis and their sexual partner(s) during prenatal care can completely prevent congenital syphilis. If detected early, congenital syphilis can be treated and decrease the chance of neonatal morbidity and mortality.
NPQIC's Congenital Syphilis Initiative aims to educate the healthcare community about increasing rates of syphilis in Nebraska, as well as ensuring that all pregnant women are tested and treated to prevent the transmission of syphilis to newborns.
Project Resources
NPQIC: Epidemic Alert Fact Sheet
National Guidance
ACOG Practice Advisory (April 2024): Screening for Syphilis in Pregnancy
Centers for Disease Control:
Penicillin G Benzathine Shortage:
- If you are having difficulty getting PCN G Benzathine for a pregnant patient, contact Pfizer directly at 800-438-1985.
CDC: State Statutory and Regulatory Language Regarding Prenatal Syphilis Screenings in the U.S. (November 2023)
ASTHO: Policy Considerations for Reducing Congenital Syphilis (May 2023)
Indian Country ECHO: Resource HUB
Patient Education
Prenatal Syphilis Screening Brochure: Protect Your Baby
Indian Country ECHO, Great Plains Tribal Leaders Health Board: Syphilis Fact Sheets
Northwest Portland Area Indian Health Board: Syphilis Resources
Office of Women's Health Fact Sheet: Protect Against Syphilis and Congenital Syphilis
Testing Resources
I Want The Kit: Free Home Test Kits

